Blockchain technology came into being in the 1990s. Satoshi Nakamoto used block chain to create Bitcoin in 2009, initiating the worldwide crypto currency boom.
The goal of this blog is to make things simple and easy to understand, For the sake of an introduction we consider that Blockchain consists of two parts: “block chain.” A block is where data is stored, whereas the chain represents the links between these blocks, creating a continuous and sequential record.
Let’s now consider the example of a ledger of a warehouse. This ledger contains numerous records of the transactions, the data of goods from when they were bought and to when they were sold, their price, where they came from, and where they went.
Table of Contents
Similarly, a blockchain functions like this ledger, Which means recording and linking data sequentially securely, and systematically. The entire series of these linked records is known as a block chain, which provides a reliable, unalterable, and transparent history of transactions.

Blockchain operates as a simple ledger system where every chunk of information is stored within a block. Each block in the block chain contains relevant data specific to its purpose.
The content of each block can vary depending on its intended use. This flexibility allows blockchain technology to be applied across different industries and scenarios, adapting the stored data to meet specific needs and functionalities.
Why do we need Blockchain?
We know that it is vital to Understand the fundamentals of block chain and its relationship to crypto currency for this sake of an argument please consider a scenario where numerous transactions take place in a regular transaction system, all of these transaction details need to be recorded in a database.
So the question arises: Is that database trustworthy? Why does this question arise in our minds? Because of the following two reasons that question its reliability:
- We do not have access to the database, we cannot independently verify the transactions due to lack of access.
- The database administrator can modify the data at any time, which would compromise its integrity and reliability making it potentially manipulatable.
So this raises the importance of adopting a decentralized system. Why? In a decentralized system, authority is distributed among all the participants rather than held by a single individual or administrator. This distribution of authority makes it more transparent and reduces the risk of corruption or manipulation. Simply, the decentralized nature of this system makes it nearly impossible to alter or modify the data once it has been recorded, significantly enhancing its reliability and trustworthiness. Blockchain technology exemplifies this system, for now, it is the only trustworthy alternative to traditional centralized systems.
What is Block Chain Technology; An Explanation
In the earlier section, we grasped the basics of blockchain in simple terms. For a better understanding, let’s delve into how blockchain operates within a crypto currency such as Bitcoin.
In the case of Bitcoin, there are three things are stored in a block Data, Hash, Previous Hash
Data: This includes essential transaction details such as the amount of Bitcoin transferred and the addresses of both the sender (entity sending the Bitcoin) and the recipient (entity receiving the Bitcoin). This data provides a complete record of the transaction.
Hash: Imagine each block in a blockchain is like a package containing information. We give each package a special fingerprint called a hash to ensure it is safe and tamper-proof. This fingerprint is created using a special math formula that takes all the details inside the package, like who sent the Bitcoin, who received it, and how much one sent or received, and writes them down into a unique code of letters and numbers. Previous Hash: This refers to the hash of the preceding block in the blockchain. Each block (except the first one, known as the genesis block) contains a reference to the previous block’s hash. This linkage creates a chain of blocks, hence the term “blockchain”.
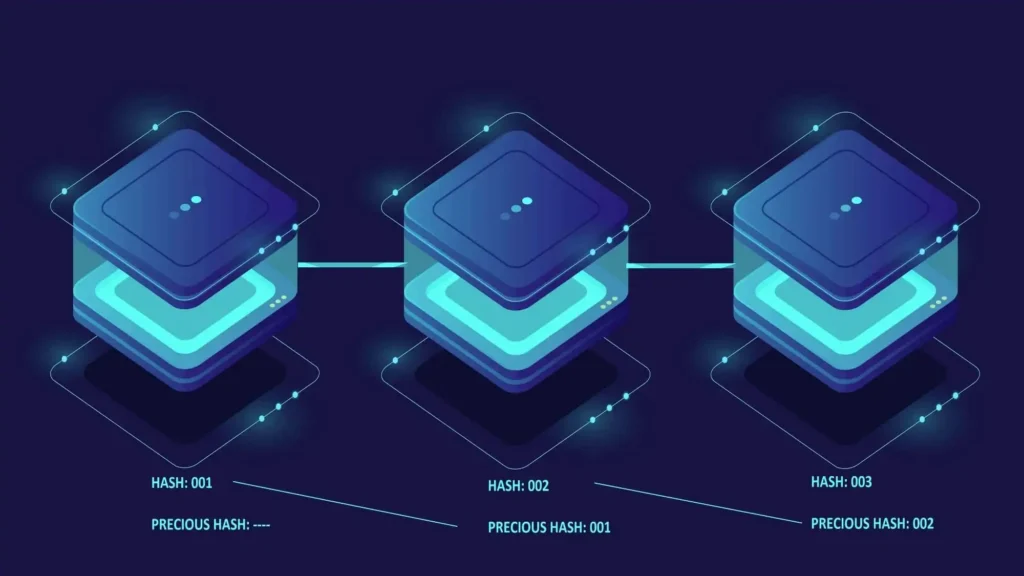
So now the hash of the previous block is saved in this block, and the hash of this block is saved in the next block making a chain known as a Blockchain. The Genesis block is the very first block of every blockchain.
What Makes Blockchain Secure? Mechanism Ensuring Trust and Reliability
As we are now familiar from the previous section with the components of the blocks, in this section we will learn about certain security protocols that are in actual the main functions of the blockchain. Understanding these protocols helps us clear the mechanism of the blockchain.
Firstly, what if someone breaches the block chain to change the data of any block? To get a better understanding let us explain the following components for you.
The hash is like a digital seal that guarantees that the package has not been tampered with. Even if someone changes just a small part of the information inside the package, the hash will change completely, alerting everyone that something is wrong. Therefore, these hashes are very important in the blockchain as they keep all information safe and reliable, ensuring that the content of each block is maintained and protected.
Whereas the previous hash maintains the order and integrity of the history of the entire blockchain. It acts as a link between blocks, creating a chain where each block has a reference to the hash of the block that came before it.
Now If someone tries to change or modify the data in a previous block, it would change that block’s hash, eventually invalidating all subsequent blocks in the chain. This alteration cascades through every block, each requiring its hashes to be updated. This process extends throughout the entire chain, which typically consists of millions of interconnected blocks. Ensuring all hashes remain consistent across such a vast blockchain is practically impossible for any single entity. This property makes the blockchain resistant to tampering and ensures the changelessness of its historical records.
Why is it impossible to change the hash and previous hash of every block?
The answer to that question is that the miners take about 10 minutes for a new block to be added to the Bitcoin blockchain, this process is called mining. Miners compete to solve complex cryptographic calculations to make each block’s hash. This process ensures that adding a new block, and thus changing its hash, is computationally expensive and time-consuming.
Moreover, once a block is added to the blockchain, changing its hash requires changing the data within that block and recalculating its hash. This change then affects the subsequent blocks because each block contains its hash and the previous block’s hash. This chaining effect means that changing one block’s hash requires changing all subsequent blocks’ hashes, making it practically impossible to modify past transactions without detection.
Therefore, blockchain security comes from a combination of cryptographic hashing, proof of work consensus methods, and the decentralized nature of blockchain networks, making them highly secure and unaffected by hacking.
Now there is another added layer of security In a blockchain network, every participant has a complete copy of the entire blockchain ledger. This ensures transparency and security because if someone wants to change a block, they must share their proposed change with everyone in the network. This process involves a Consensus mechanism where all participants vote on whether the proposed change is valid or invalid.

Here’s how it works: When someone proposes a change to a block, everyone in the network verifies the change against their copy of the blockchain. Suppose the majority of the network agrees that the proposed change is accurate and valid according to the blockchain rules (such as cryptographic integrity and transaction rules). In that case, the change is accepted and implemented.
This consensus mechanism is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. It ensures that no single entity can alter the blockchain arbitrarily. Even if someone attempts to add a new block or modify existing data, they must follow the consensus rules and obtain approval from the majority of the network. This process not only secures the blockchain against fraud and tampering but also ensures that all participants in the network reach an agreement on the state of the blockchain at all times.
The aforementioned features of blockchain make it easy to track the history of transactions and make it difficult to modify or change the information of blocks of blockchain, thus making it a more reliable and trusted system.
What are the Blockchain Applications?
As we know Block chain can be used for the storage and processing of information, safety assurance, and security. Here are some example applications of Blockchain other than crypto.

In Supply Chain Management, Blockchain can be used to track the journey of products from their origin to the consumer in a very transparent process. This transparency ensures authenticity, fraud prevention, and ethical sourcing.
Blockchain in Financial Services can also be used to transfer payments over a long distance faster and more securely It can be used for smart contracts automated transactions, and transparent auditing.
So Healthcare can also be an application of blockchain, it can be used to keep patient records, to secure and streamline medical data sharing among healthcare providers while ensuring patient privacy and data integrity.
Blockchain could be a revolutionary step in Electronic Voting Systems It can enhance the security and transparency of voting processes, The system provided by block chain is a tamper-resistant record of votes for sure.
Smart Real Estate Management as it is obvious from the heading Blockchain can authenticate and protect intellectual property rights by creating immutable records of ownership and transactions.
Legal Contracts could be another use-case of Block chain based smart contracts to automate and enforce agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries and ensuring contract terms are met transparently.
Now we know from these applications that blockchain is versatile, it can enhance security, transparency, and efficiency across various sectors far beyond financial transactions.
Conclusion
In this blog, we delved into the basics of Blockchain and cryptocurrency as its use-case in very simple words with a shop ledger example, We have explored the components of block chain and the concept of how every block in the block chain contains data, Which means a unique hash, and the previous block’s hash, creating a secure and tamper-evident sequence.
We have also learned how decentralization ensures that “all participants have access to the same data, fostering trust and transparency”. Whereas consensus mechanisms further enhance the integrity of the blockchain by ensuring that all transactions are verified and agreed upon by the network hence ensuring the reliability of the blockchain.
Its ability to provide security, transparency, and immutable records makes it a powerful tool for applications beyond crypto currency, including supply chain management, financial services, healthcare, and more. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its impact on enhancing data security, transparency, and efficiency will only grow, cementing its role as a cornerstone of the digital age.
Thank you for embarking on this journey to answer the question of what is the block chain technology! Together, we’ve explored how its unique composition ensures unparalleled security, transparency, and reliability.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business leader, or simply curious about the future, we hope you’ve gained valuable insights into how blockchain revolutionizing various industries. We value your thoughts and encourage you to provide us with feedback to help us improve and continue delivering content that matters to you. Stay tuned as we continue to delve deeper into the innovations that are shaping our digital landscape.
FAQs
1. What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized technology that records transactions on various computers. It consists of blocks (data storage units) linked in a chain, ensuring secure, transparent, and tamper-evident records.
2. Who created blockchain technology?
Block chain technology was conceptualized in the 1990s, but it gained significant attention when Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin in 2009 using blockchain.
3. How does a blockchain work?
A blockchain works by recording data in blocks, each containing transaction details, a unique hash (a digital fingerprint), and the previous block’s hash. This structure ensures that any change to a block alters its hash, making tampering evident and maintaining the chain integrity.
4. Why is blockchain considered secure?
It uses cryptographic hashing, proof-of-work consensus methods, and a decentralized network of participants. These elements make it nearly impossible to alter records without detection, ensuring data integrity and trustworthiness.
5. What are decentralized system advantages?
A decentralized system distributes authority among all participants rather than a single entity, enhancing transparency, reducing corruption, and minimizing the risk of data manipulation, making the system more reliable and trustworthy.
6. What is the role of miners in a blockchain?
Miners compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to add new blocks to the blockchain. This process, known as mining, ensures that blocks are added securely and that altering any block would require immense computational power, making tampering impractical.
7. How does the consensus mechanism work in a blockchain?
The consensus mechanism ensures that all participants in the network agree on the state of the blockchain. When a change is proposed, it must be verified and approved by the majority of the network, maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain.
8. What are some applications of blockchain technology beyond cryptocurrency?
Blockchain technology can be used in various industries, including:
- Supply Chain Management System: Tracking product origins and ensuring transparency.
- Financial Services: Secure and fast long-distance payments, smart contracts, and transparent auditing with minimal fees, unlike conventional banking.
- Healthcare Systems: It stores, shares, and maintains medical records securely.
- Election Voting Systems: It enhances the security and transparency of elections because of its decentralized nature.
- Real Estate Management system: Authenticating property rights and transactions.
- Legal Contracts: Automating and enforcing agreements through smart contracts.
9. Why is blockchain technology important?
Blockchain technology is important because it provides a secure, transparent, and tamper-evident method for recording and verifying transactions. Beyond just cryptocurrencies, it can enhance efficiency, security, and transparency in several sectors.
10. How can I learn more about blockchain technology?
To learn more about blockchain technology, you can explore resources such as online courses, webinars, and articles from reputable sources. Our blog also offers in-depth guides and analysis to help you understand and navigate the block chain world.

